TI01: C-ITS Local Broadcast
Use short range communications to broadcast traveler information only within the local area where that information is relevant.
Relevant Regions: Australia, Canada, European Union, and United States
- Enterprise
- Functional
- Physical
- Goals and Objectives
- Needs and Requirements
- Sources
- Security
- Standards
- System Requirements
Enterprise
Development Stage Roles and Relationships
Installation Stage Roles and Relationships
Operations Stage Roles and Relationships
(hide)
| Source | Destination | Role/Relationship |
|---|
Maintenance Stage Roles and Relationships
Functional
This service package includes the following Functional View PSpecs:
| Physical Object | Functional Object | PSpec Number | PSpec Name |
|---|
Physical
The physical diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG.Physical diagrams have not been developed for this application yet.
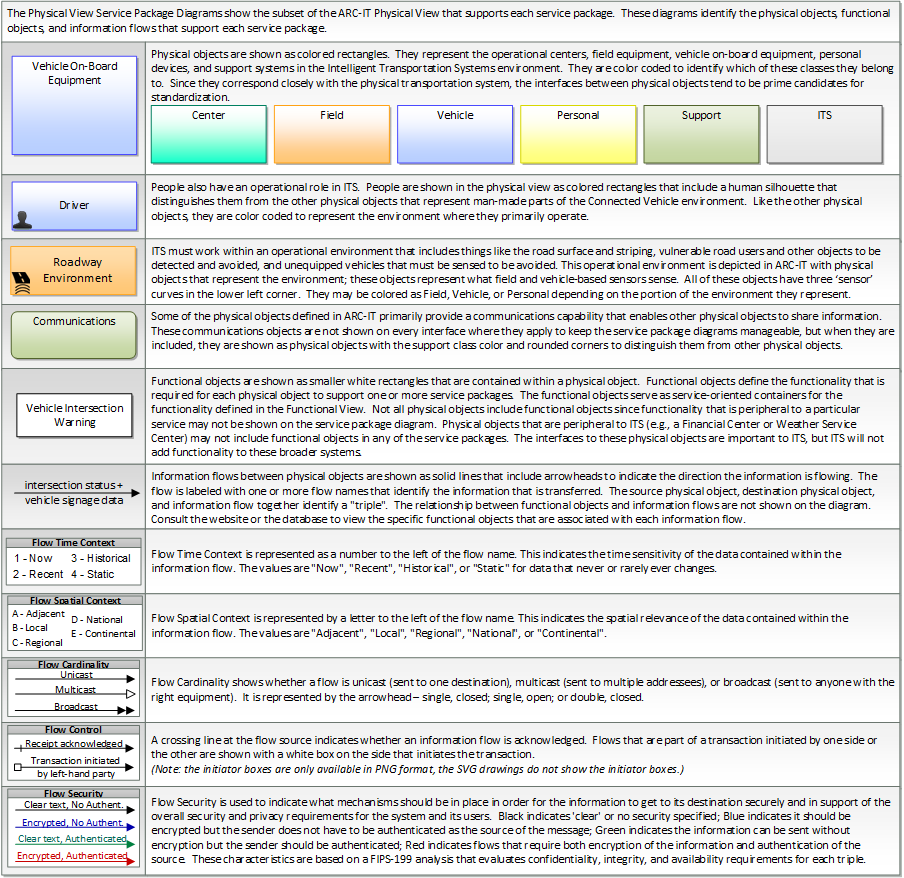
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|
Includes Functional Objects:
| Functional Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|
Goals and Objectives
Associated Planning Factors and Goals
| Planning Factor | Goal |
|---|---|
| A. Support the economic vitality of the metropolitan area, especially by enabling global competitiveness, productivity, and efficiency; | Improve freight network |
| B. Increase the safety of the transportation system for motorized and nonmotorized users; | Reduce fatalities and injuries |
| D. Increase the accessibility and mobility of people and for freight; | Reduce congestion |
| E. Protect and enhance the environment, promote energy conservation, improve the quality of life, and promote consistency between transportation improvements and State and local planned growth and economic development patterns; | Protect/Enhance the Environment |
| F. Enhance the integration and connectivity of the transportation system, across and between modes, for people and freight; | Enhance integration and connectivity |
| G. Promote efficient system management and operation; | Improve efficiency |
| I. Improve the resiliency and reliability of the transportation system and reduce or mitigate stormwater impacts of surface transportation; | Improve resiliency and reliability |
| J. Enhance travel and tourism. | Support travel and tourism |
Associated Objective Categories 
Associated Objectives and Performance Measures 

Since the mapping between objectives and service packages is not always straight-forward and often situation-dependent, these mappings should only be used as a starting point. Users should do their own analysis to identify the best service packages for their region.
Needs and Requirements
| Need | Functional Object | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Related Sources
- None
Security
In order to participate in this service package, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | ||||
In order to participate in this service package, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | |||||
Standards
Currently, there are no standards associated with the physical objects in this service package. For standards related to interfaces, see the specific information flow triple pages.
Needs and Requirements
| Need | Functional Object | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
System Requirements
| No System Requirements |